River, Lake Fishing in Anderson
Lake Hartwell Half Day
Cape May Inshore Trip
Lake Of The Ozarks Pro Fishing
Inshore Fishing in Stone Harbor
Nighttime Bridge Hopping Trip
Inshore Fishing in Stone Harbor
Screaming Drag Surf Fishing
Inshore, Nearshore Fishing in Stone Harbor
Stone Harbor Inshore/Nearshore
New Jersey On Light Tackle
Inshore, River Fishing in Somers Point
Inshore Striped Bass
Inshore, Nearshore, River in Keyport
Striped Bass - Raritan Bay & Ocean
Inshore Fishing in Ocean Township
8hr Inshore
We started Captain Experiences to make it easy to book fishing and hunting guides around the world. With over 2,000 Damn Good Guides, our platform makes finding and booking a trip seamless. Head here to check out our trips.
Panfish is a term coined by anglers to describe a handful of fish that are delicious and are roughly small enough to fit into a pan. The fish species that are included when someone mentions panfish largely depends on the region they are fishing. However, five species of fish almost always make the list. Here’s everything you need to know about these five popular panfish.
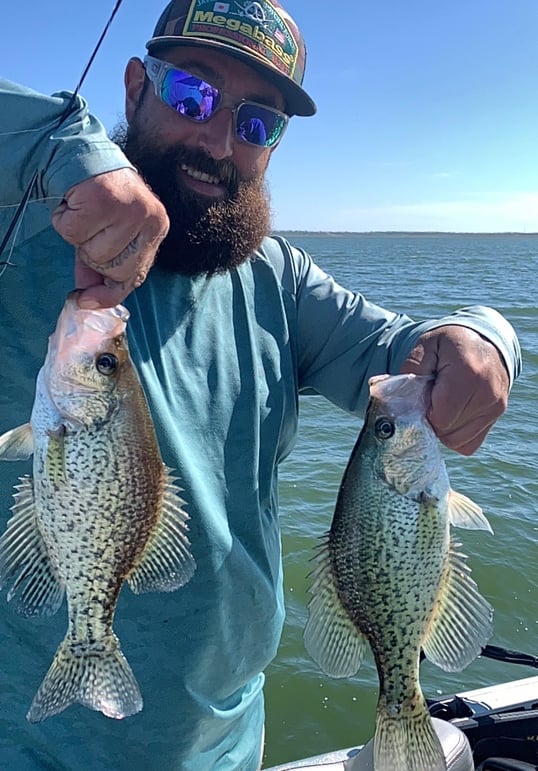

Crappie
Chances are if you grew up fishing in the southern half of the U.S. crappie were one of the fish you routinely pursued for their meat. The fish are similar in shape to sunfish only much larger and with a monotone color scheme. While at first glance these fish might not look like much of a prize, crappie have sweet, mild, white meat that flakes easily once cooked. Common preparations include frying, steaming, or grilling and are served with vegetables. Crappie are an ambush predator that holds up in brush piles in moderately shallow water. Using small jigs or live bait are the best ways to get a bite and enjoy the fiery fight and a delicious meal.
Yellow Perch
The yellow perch, commonly referred to as simply “perch”, is a freshwater perciform fish native to the midwest and northeast United States and much of Canada. Known for their vibrant green and gold coloration with black stripes, these fish are physically and genetically similar to the European perch and is sometimes considered a subspecies. Yellow perch are prey for larger fish but they are also predators when they reach adulthood. Various names for yellow perch have become prominent across their range including lake perch, American perch, raccoon perch, ringed perch, dodd fish, and striped perch.
Yellow Perch typically range from four to twelve inches long but have been known to grow larger. The world record yellow perch 4 lb 3 oz was caught in 1865 in New Jersey, and is the longest-standing record for freshwater fish in North America.
Yellow perch habitat consists of vegetated shoreline waters and relatively shallow structures. Perch tend to form dense schools in shallow vegetation, because of their preference for small, weed-filled bodies of water. On rare occasions, yellow perch can be found in water deeper than 50 feet. Perch population can survive but are less abundant in deep, clear, open bodies of water. River populations of perch school up in protected waters just out of the current and moderately vegetated areas.
The ideal temperature range for catching yellow perch is between 63 to 77 degrees. However, yellow perch have faster growth rates when water temperatures range between 70 and 75 degrees. If water temperatures exceed 78 degrees yellow perch will be stressed and the bite will fall off. Catching fish in warmer waters also increases the likelihood of death after release.
Blue Gill & Sunfish
Bluegill are a popular freshwater game fish throughout the United States. They have been introduced to many freshwater lakes, ponds, rivers, and streams and are distributed throughout the western United States. Bluegills live in shallow water but often go into deep weed beds in search of food or with the purpose of spawning. In the wild, they swim together in schools of 10 to 20 fish. The bluegill growth rate depends on the type and amount of food it eats. Their small mouths allow them to eat small and microscopic creatures.
Bluegills inhabit slow and slack waters in rivers and lakes. Their preferred environment consists of shallow water and dense aquatic plants. Fallen logs, rocks, and weed beds provide the bluegill and other sunfish protection from predators and a place to find food. Smaller and younger bluegill rarely leave cover but larger adults will swim in open water. In the warm summer months, these fish move to deeper cooler waters and suspend just above the bottom. In the mornings, bluegill will push into the shallows to warm up.
Bluegills are schooling fish that commonly travel in groups of 12 to 30. Bluegill schools also contain various other species of sunfish like sunfish, smallmouth bass, crappie, and pumpkinseed. Bluegill individuals in the same school hunt prey together but also use their numbers to protect against predators. Bluegill and most sunfish naturally live four to six years but can reach up to 11 years old in captivity.
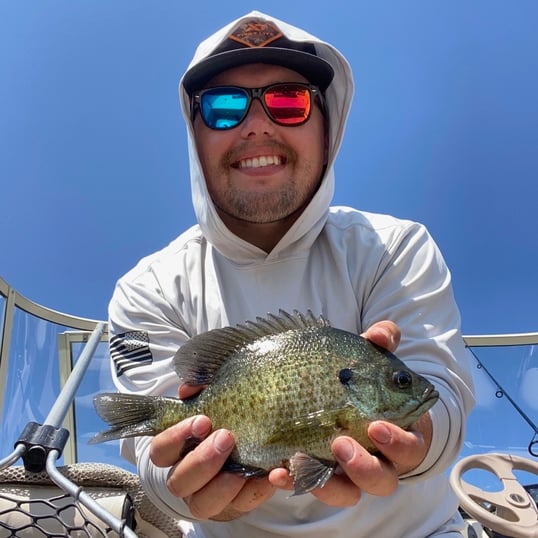

Bluegills and most sunfish share the same general tall and compressed body characteristics. These fish have relatively flat bodies with a slightly forked tailfin. One of the most identifiable features of this fish is their spiny dorsal fin which can be painful when handling them.
The bluegill gets its name from their blue cheeks and gill plates. They also have a yellow midsection similar to many species of sunfish. Bluegills can also present green vertical bars on down the sides of their body when threatened. On the back edge of their gills, bluegills have a large black spot commonly called the ear, which helps differentiate them from other sunfish like redear sunfish.
Other similar species that are grouped together as panfish include:
Green sunfish Redear sunfish Redbreast sunfish Spotted sunfish Pumpkinseed Warmouth
Yellow Bass
This fish is considered similar to White Bass and Striped Bass. Like the other bass, this fish is predominately silver in color with horizontal black stripes that run the length of their body. The lower stripes are broken on yellow bass and are one of the defining characteristics that separate them from white bass. The backs of this fish are gray-green in color but also feature yellow eyes and belly. Another differentiating feature of yellow bass is their lack of tongue or teeth.
Yellow Bass are commonly found in slow-moving freshwater rivers and lakes. The native distribution of the yellow bass extends through the Mississippi River system from Minnesota to Louisiana. It is found in areas with dense vegetation and low turbidity.
Yellow bass typically only reach about a foot long. In order to survive out in open water, these fish live and hunt in large schools. Common food sources for Yellow Bass include some crustaceans, insects, and smaller fish. The lifespan of these pin-sized predators is up to seven years. The maximum size for a yellow bass is approximately 18 inches long and around two pounds.
Joey Butrus
Updated on June 22, 2023

April 26, 2022

June 3, 2021

June 22, 2022
July 1, 2024

August 21, 2023
Related Articles
February 28, 2022
July 26, 2022
April 4, 2022
Featured Locations
- Fishing Charters Near Me
- Austin Fishing Guides
- Biloxi Fishing Charters
- Bradenton Fishing Charters
- Cabo San Lucas Fishing Charters
- Cancun Fishing Charters
- Cape Coral Fishing Charters
- Charleston Fishing Charters
- Clearwater Fishing Charters
- Corpus Christi Fishing Charters
- Crystal River Fishing Charters
- Dauphin Island Fishing Charters
- Daytona Beach Fishing Charters
- Destin Fishing Charters
- Fort Lauderdale Fishing Charters
- Fort Myers Fishing Charters
- Fort Walton Beach Fishing Charters
- Galveston Fishing Charters
- Gulf Shores Fishing Charters
- Hatteras Fishing Charters
- Hilton Head Fishing Charters
- Islamorada Fishing Charters
- Jacksonville Fishing Charters
- Jupiter Fishing Charters
- Key Largo Fishing Charters
- Key West Fishing Charters
- Kona Fishing Charters
- Lakeside Marblehead Fishing Charters
- Marathon Fishing Charters
- Marco Island Fishing Charters
- Miami Fishing Charters
- Montauk Fishing Charters
- Morehead City Fishing Charters
- Naples Fishing Charters
- New Orleans Fishing Charters
- New Smyrna Beach Fishing Charters
- Ocean City Fishing Charters
- Orange Beach Fishing Charters
- Panama City Beach Fishing Charters
- Pensacola Fishing Charters
- Pompano Beach Fishing Charters
- Port Aransas Fishing Charters
- Port Orange Fishing Charters
- Rockport Fishing Charters
- San Diego Fishing Charters
- San Juan Fishing Charters
- Sarasota Fishing Charters
- South Padre Island Fishing Charters
- St. Augustine Fishing Charters
- St. Petersburg Fishing Charters
- Tampa Fishing Charters
- Tarpon Springs Fishing Charters
- Venice Fishing Charters
- Virginia Beach Fishing Charters
- West Palm Beach Fishing Charters
- Wilmington Fishing Charters
- Wrightsville Beach Fishing Charters


































